There was an interesting internal thread that I came across yesterday where someone was asking if VMware Fusion supported memory overcommitment like VMware Workstation? In VMware Workstation, memory overcommitment can be adjusted by going to Edit->Preferences->Memory which provides three different options as shown in the screenshot below. This setting specifies the percentage of memory that would be reserved from the physical host memory for each Virtual Machine.

These options map to the following % of host memory reservation:
| Option | % of Host Memory Reserved Per VM |
|---|---|
| Fit all virtual machine memory into reserved host RAM | 100 |
| Allow some virtual memory to be swapped | 50 |
| Allow most virtual memory to be swapped | 25 |
Disclaimer: Be aware, that default safe guards have been put in place to ensure optimal VM performance. If you decide to change these settings and allow memory overcommitment, it can potentially degrade performance of both your VMs as well as host system. Make sure you understand the changes before applying them.
You can also specify a custom value by editing the VMware Workstation configuration file located in: C:\ProgramData\VMware\VMware Workstation\config.ini and modifying or adding the following property:
prefvmx.minVmMemPct = P
where P is the percentage of configured VM memory that should fit into the host memory. The smallest value that P can be is 1. Below is a screenshot of a 32GB VM running on a Macbook Air with latest version of Fusion (8.5.3) which only has 8GB of physical memory and the value that I had used for this demonstration is 1.
Going back to VMware Fusion, memory overcommitment is also possible but the option to configure it is not available in the VMware Fusion UI. You will need to add the above setting into the VMware Fusion configuration file located in /Library/Preferences/VMware\ Fusion/config which does not exist by default. You will need to restart Fusion/Workstation for the change to go into effect.
In addition to the change, if you do decide to overcommit your memory, it was also mentioned that you may also want to disable Hard Disk buffering for optimal performance. You can make this change in the Advanced Settings of the the VM as seen in the screenshot below.
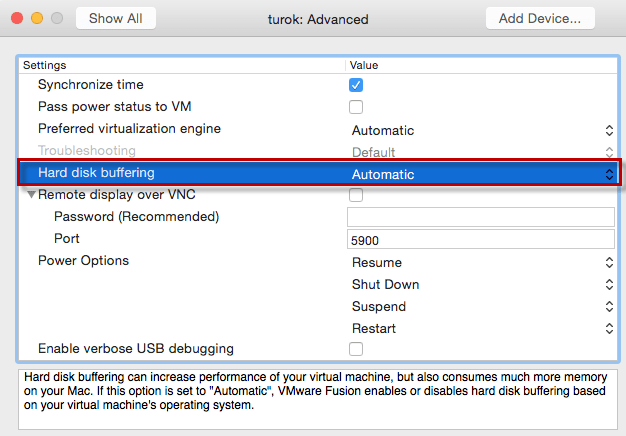
You can also just add the following property to the Virtual Machine's VMX configuration file:
hard-disk.hostBuffer = "disabled"
Memory commitment can be a wonderful tool, especially for lab environments. If you combine this with SSD storage and if swapping does occur, the impact may be acceptable so that you can run a few more VMs. Thanks to Regis Duchesne & Jesse Pool for sharing this handy tidbit!


