When enabling VSAN, users have the option to specify how the disks (SSD/HDD) will be added to VSAN either automatically (recommended) or manually claimed by the end user.

If you decide to manually claim your disks on each ESXi host within the VSAN cluster, then you will probably need to figure out which disks are SSD and HDD for you to create your VSAN disk groups. If you have used the vSphere Web Client to perform this operation, you will notice there is a toggle for displaying "eligible" disks for VSAN which can also be obtained programmatically using the vSphere API.

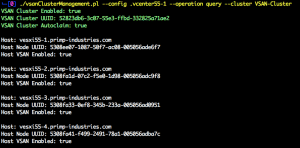
On each ESXi host, there is a vsanSystem manager that provides various methods for disk management and the one that we are interested in is called QueryDisksForVsan(). To demonstrate this functionality, I have created the following sample vSphere SDK for Perl script called vsanQueryDisksForUse.pl. The script will query each ESXi host in a vSphere Cluster and return a list of disks which specifies if they are eligible for use with VSAN and whether the disk is an SSD or not.
Disclaimer: These scripts are provided for informational and educational purposes only. It should be thoroughly tested before attempting to use in a production environment.
To check for the list of available SSD/HDD, run the following command:
./vsanQueryDisksForUse.pl --server vcenter55-1 --username root --cluster VSAN-Cluster

Using this information, you can then use the AddDisks_Task() method to create your own VSAN Disk Groups on each ESXi host. As you can see, it is a couple more steps if you opted for manual mode and I would recommend letting the vSphere platform automatically take care of this for you.
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 1 – Enable VSAN Cluster
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 2 – Query available SSDs
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 3 – Enable VSAN Traffic Type
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 4 – VSAN Disk Mappings
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 5 – VSAN Host Status
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 6 – Modifying Virtual Machine VM Storage Policy
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 7 – VSAN Datastore Folder Management
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 8 – Maintenance Mode
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 9 – VSAN Component count
- Exploring VSAN APIs Part 10 – VSAN Disk Health