It looks like we just got an early Christmas gift from Etienne, George and the VMware Flings team with the release of v4 of the ESXi Embedded Host Client (EHC). One of the new features that I am most excited about is the ability to upgrade ESXi itself using the "Update" feature which was first introduced in EHC v3. In the previous release of EHC, you could install or patch any ESXi VIB using this interface which I had blogged about here. With the latest release, Etienne has expanded its functionality to not only allow for a VIB URL but also a metadata.zip URL which ESXi offline bundles contain.
Here is an example of using EHC v4 to upgrade an ESXi 6.0 host to ESXi 6.0 Update 1:
Step 1 - Download ESXi offline bundle of choice, in this example we are downloading the offline bundle for ESXi 6.0 Update 1: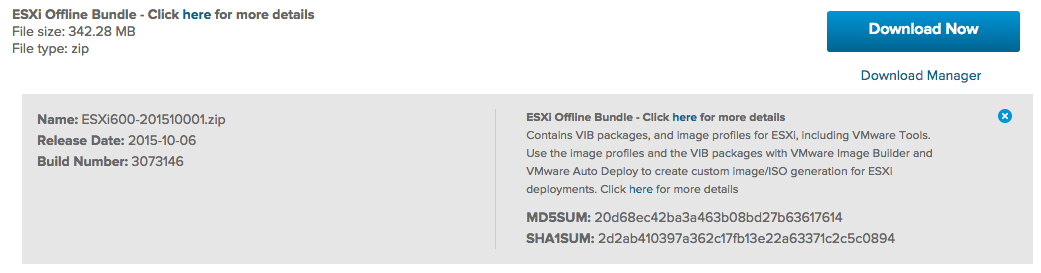
Step 2 - You will need to extract the contents of the offline bundle and then upload the content to either a vSphere Datastore or an HTTP accessible URL as shown in the screenshots below.

Currently it is not possible to upload an entire directory using the Datastore Browser with EHC. This is something I have reported internally and hopefully will be fixed in a future update.

Step 3 - Click on the "Help" menu on the upper right hand corner of the Embedded Host Client and select the "Update" option which should prompt you to specify a URL. You can either specify a local datastore path to the metadata.zip such as the following:
/vmfs/volumes/datastore1/ESXi600-201510001/metadata.zip
or you can specify an HTTP(s) URL to the metadata.zip like the following:
http://192.168.1.180/ESXi600-201510001/metadata.zip

Step 4 - Once you click the "Update" button, you will be asked to confirm and then you should see task kicked off called "Install Host Patch V2". Once the task has completed, you will need to reboot the ESXi host for the changes to take effect. If you are interested in viewing the update logs without having to log in via SSH, you can click on the "Monitor" tab of the Host option and under "Logs", click on /var/log/esxupdate.log to see the progress.

If you have more than one or two hosts, I definitely recommend uploading the extracted offline bundle onto a webserver or a shared vSphere Datastore which you can the access from multiple ESXi hosts. This is a very nice way to easily upgrade your ESXi hosts without having to go into the ESXi Shell or enable SSH. Pretty neat feature if you ask me! There are many other new enhancements included in this release, be sure to give them a try and let us know if you have any feedback by leaving a comment on my blog or better yet, directly on the Fling site.
What's new in Embedded Host Client v4
- Host
- Ability to change host acceptance level
- Ability to edit lock down exception users
- Ability to edit system swap settings
- VM
- VM list has been optimized for performance, reducing data download by a factor of 5.
- Ability to edit VM advance options
- Ability to edit VM video adapter settings
- Add a PCI pass through device (unable to remove device though)
- SRIOV support for Network card devices
- Ability to change browser console keyboard layout (Japanese and German are the currently supported layouts)
- Cmd+a or Ctrl+a to select all VMs in list
- Soft-power off and reset if Tools is installed is now supported
- General
- New Tools and links menu under Help
- Update mechanism can now take a URL or data store path to an metadata zipfile, allowing to update ESXi itself
- Localization and internationalization (French, Spanish, Japanese, German, Chinese (traditional and simplified) and Korean
- Ability to disable session timeout
- A huge number of bugfixes and minor improvements



