Today, I am very happy to announce that we have released the official Windows vCenter Server to vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) Migration Tool which is part of the new VCSA vSphere 6.0 Update 2m release! I know many of you have been asking for an update since we released the VCS to VCSA Convert Appliance Fling a little over a year ago. The Fling was pretty limited in functionality and this was by design so that we could quickly get something out to our customers and get some early feedback. Although I could not say anything, the VMware Engineering team have been very hard at work incorporating all of the feedback in how they designed and built the official VCSA Migration Tool that you see today.
With that, I would like to extend a huge thanks to all of our customers who took part in the Fling and provided feedback both in the comments section as well as reaching out to me through the various channels. It was great to engage with literally hundreds of customers of all sizes and segments, all looking to move away from a Windows-based vCenter Server to the VCSA. Lastly, I want to thank our VMware Engineering team, both to the folks who lead the initial effort on the Fling prototype to those who then productized it! I was very fortunate to have been part of this amazing milestone at VMware.

The VCSA Migration Tool workflow is quite different from how the Fling had worked which hopefully customers will appreciate. The team worked really hard on trying to simplify the overall user experience as well as trying to minimize the overall amount of downtime for the migration. In addition, we have also added full support for additional configurations and deployment topologies which you can find more details in the resource link below which includes an FAQ which I *highly* recommend folks have a look at before starting or asking further questions.
Collection of all #migrate2vcsa Links / Resources: vmwa.re/migrate2vcsalinks
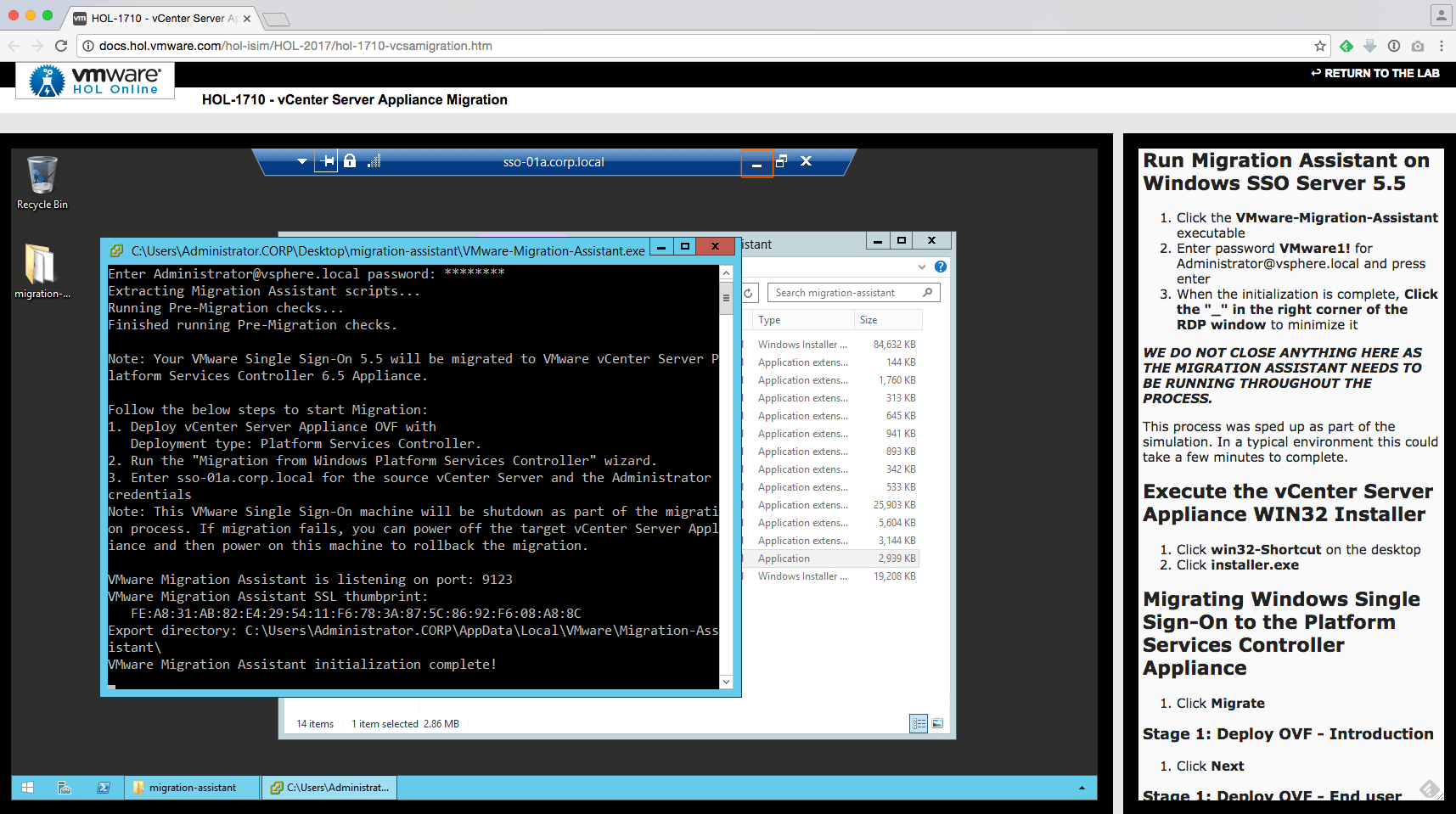
Here is a quick video that I had recorded earlier which demonstrates a migration from a Windows vSphere 5.5 environment to VCSA 6.0 Update 2m, hopefully this will give you a nice overview of the migration process.
[UI Demo] - Migration of Windows vCenter Server 5.5 to vCenter Server Appliance 6.0 Update 2m from lamw on Vimeo.
One last thing I want to quickly mention is that this release is specifically targeted at customers looking to migrate from a Windows vCenter Server 5.5 to the VCSA 6.0 Update 2, hence the letter "m" denotation. If you are NOT looking to migrate your Windows vCenter Server to the VCSA, this release is NOT applicable to you as you will NOT be able to perform a new install and/or upgrade using this release. Instead, you should be looking at the vSphere 6.0 Update 2 release which is the exact same code base that vSphere 6.0 Update 2m is based off of. This will be even more apparent when you launch the VCSA Installer, as the "Migrate" button is the only option as shown in the screenshot below.

For those planning to attend VMworld this year, we do plan to have several sessions covering the new VCSA Migration Tool as well as some other surprises 🙂 I hope to see you there and if you have any comments or feedback, feel free to leave it here or use the #migrate2vcsa hashtag if you are on Twitter, especially if you are interested in some of the surprises at VMworld.